Excavation trench safety is critical for saving lives on the building site. Trenches risk collapse as well as other dangers, including falling debris, which can cause serious injury or death. According to the OSHA, it accounts for more than 100 deaths every year during trenching and excavation operations. This article will guide you through essential trench protection methods, compliance with OSHA regulations, and best practices for ensuring trench safety.

What is Excavation Trench Safety?
Excavation trench safety refers to the measures and precautions taken to prevent accidents during trenching and excavation work. Trench work typically involves digging trenches deeper than they are wide, often for utility installation or foundation work. Due to the confined nature of trenches, they pose significant risks, especially from cave-ins, falling tools, and equipment.
Safety standards for excavation trench work are outlined by OSHA trench and excavation regulations. These rules ensure that trenching operations are performed safely, minimizing hazards to workers in and around the trench.
Understanding OSHA’s Excavation and Trench Regulations
What is Considered a Trench by OSHA?
According to OSHA, a trench is defined as any narrow excavation made below the surface of the ground that is deeper than it is wide, with a width typically not exceeding 15 feet. A trench is different from a regular excavation because of its relatively narrow width about its depth. OSHA sets strict safety standards for trenches to ensure that they are adequately protected to prevent accidents.
OSHA’s regulations are clear that any trench deeper than 5 feet requires protective systems. These systems are designed to prevent trench collapses and minimize the risk of injury.
Key OSHA Regulations for Trenching
- Excavation Protection: OSHA mandates that employers must provide protective systems for trenches over 5 feet deep. The protection must be designed based on the soil type, depth, and conditions at the job site.
- Trench Safety Systems: OSHA specifies the use of trench boxes, shoring, and shielding as approved protection methods for trenches.
- Competent Person: A “competent person” is required to inspect trenches daily before workers enter, ensuring that the trench is safe.

What is Trench Protection?
Trench protection refers to the system or method used to prevent trench collapses, protect workers from falling debris, and ensure the stability of trench walls. These protection systems are critical for maintaining the safety of workers who are exposed to hazardous trench environments.
Several trench protection methods are used in the industry, including shoring, shielding, benching and sloping.
Types of Trench Protection Systems
1. Shoring Systems
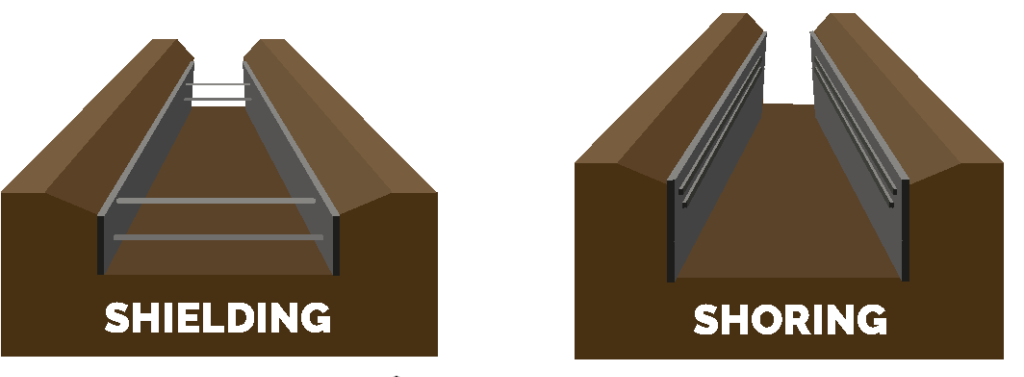
Shoring is a method used to support the walls of a trench by installing a system of beams, braces, and planks. This system helps prevent trench collapses by keeping the trench walls from caving in under pressure. Shoring systems are particularly effective for deeper trenches or when the soil is loose and unstable. The most common types of shoring include hydraulic shoring, timber shoring, and pneumatic shoring.
- Hydraulic Shoring: Uses hydraulic jacks to apply pressure against the trench walls to prevent collapse. It’s quick to install and is ideal for deeper trenches.
- Timber Shoring: Involves using timber beams and posts to brace the trench. This is a more traditional and cost-effective solution, but it may not be suitable for all soil conditions or depths.
- Pneumatic Shoring: Uses air pressure to create stability and prevent trench wall movement. It’s often used for shallow trenches with unstable soils.
2. Shielding Systems
Shielding, also known as trench boxes, involves using a protective structure made from steel or aluminum placed in the trench to protect workers inside from falling debris and soil collapses. Unlike shoring, which supports the trench walls, shielding is a containment system that provides a safe space for workers inside the trench.
Trench boxes are typically used when the trench is not particularly deep but still poses risks. These systems are easy to install and can be moved as work progresses, providing flexibility on the job site.
- Trench Boxes: These are large, box-like structures that are lowered into the trench. Workers can stand inside the box, and the surrounding earth is less likely to collapse into the protected space.
3. Benching Systems
Benching involves creating a stepped structure along the walls of the trench, with each step sloping back toward the surface. This system is typically used in trenches where the soil is stable enough to support the steps. Benching is effective for shallow trenches with stable soil conditions but may not be suitable for deeper excavations.
- Shallow Trench Work: Benching is most effective when the trench is not excessively deep, and the soil is stable. It reduces the risk of soil collapse by redistributing the weight in a stepped manner.
- Limited Use: Benching is not recommended in trenches deeper than 20 feet, as the risk of soil slippage increases.
4. Sloping Systems
Sloping involves cutting the sides of the trench at an angle so that the walls gradually slope back toward the surface, preventing the trench from collapsing. This method works best in stable soils where the trench is shallow or moderately deep. The angle of the slope depends on the type of soil, with softer soils requiring a steeper angle to prevent collapse.
- Soil Type Dependent: The angle of the slope is determined by the type of soil in the trench. For example, for stable sandy soil, the trench may need to be sloped at a 1:1 ratio (45-degree angle), while softer soils may require a gentler slope to ensure stability.
- Shallow to Moderate Depths: Sloping is best used for trenches that are not too deep, as it becomes more difficult to achieve a stable slope with increasing depth.

The Importance of Trench Wall Support
Trench wall support is another essential aspect of excavation trench safety. Trench walls are highly susceptible to collapse due to soil movement, and providing adequate support is crucial to prevent such incidents. Trench wall support systems help stabilize the trench by ensuring that the walls remain intact and do not cave in under pressure.
Types of Trench Wall Support Systems
- Hydraulic Shoring: Utilizes hydraulic systems to brace the trench walls and prevent collapse.
- Timber Shoring: Uses timber beams and posts to support trench walls. This system is effective in areas with stable soil conditions but may not be suitable for deeper or unstable trenches.
- Vertical Shoring: This system involves placing vertical shoring along the trench walls to prevent them from bowing inwards.
Best Practices for Trenching Safety
Ensuring trench safety requires a combination of training, proper protective systems, and regular inspections. Below are some best practices for excavation trench safety that every construction manager and worker should follow:
1. Conduct Pre-Job Safety Planning
Before beginning any trenching work, a thorough risk assessment should be conducted. This includes evaluating soil conditions, trench depth, and the potential for water accumulation. Proper planning helps determine the most effective protection methods and ensures that workers are fully prepared for the job.

2. Use Trench Protection Systems
As per OSHA trench protection requirements, any trench deeper than 5 feet must be protected with a suitable system. Common trench protection systems include:
- Shoring: To prevent trench wall collapse.
- Shielding: Using trench boxes to protect workers.
- Trench Boxes: To prevent the collapse of trench walls and provide a safe working space.
3. Regular Inspections
OSHA trench and excavation regulations require that trenches be inspected daily before workers enter. A competent person should perform these inspections to check for potential hazards such as soil instability, water accumulation, or unsafe trench walls.
4. Provide Worker Training
Training workers on how to recognize potential hazards in trenches is crucial for safety. Workers should be educated on how to use trench protection systems properly and understand the risks involved in trench work.
5. Ensure Proper Access and Egress
Workers should have a safe means of entering and exiting the trench. A ladder or other secure means of access should be placed within 25 feet of any worker in the trench to ensure quick evacuation in an emergency.
Conclusion
Excavation trench safety is an essential part of any construction project involving trenching. By following OSHA trench and excavation regulations and employing the right trench protection systems, workers can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Shoring, shielding, and trench boxes are all effective methods for ensuring the safety of workers in trenches. However, compliance with safety standards, regular inspections, and proper training are key to preventing tragedies on the job site.






